New to NetSuite Revenue processing?
Advanced Revenue Management automates revenue forecasting, allocation, recognition, reclassification, and auditing through a rule-based event handling framework. It is compliant with the ASC 606 revenue standard.
With advanced revenue management you can defer revenue for recognition across future periods according to the rules you configure. It supports fair values based on vendor-specific objective evidence (VSOE), best estimate of selling price (ESP), third party evidence (TPE), and other fair value methods your company uses.
The following records and transactions are used in advanced revenue management:
- Revenue arrangements–Transactions that record the details of customer obligations for purposes of revenue allocation and recognition. The new engine for revenue automatically creates revenue arrangements from predefined revenue sources, such as sales transactions, or straight from an invoice. The arrangements from multiple revenue sources can be consolidated.
- Revenue elements– These are records that correspond to individual lines in a source transaction. Revenue elements are attached as lines on a revenue arrangement. If you have just one item on the transaction, there will be one element.
- Revenue recognition rules– The rule records the revenue schedule assigned to the item with the recognition method, amount source, and the start and end date sources. If an item has more than one ‘rule’ this can be edited during the revenue processing.
- Revenue recognition plans– These are records that indicate the posting periods in which revenue should be recognized and the amount to be recognized in each period. Revenue plans are derived from revenue recognition rules. Each revenue element has a forecast plan and one or more actual plans. The actual revenue plans control the posting of revenue. This plan can be changed to accommodate multiple revenue recognition time lines and methods.
- Fair value price list– list of the records that define the fair value for items. Fair value price is used to allocate revenue in revenue arrangements.
There are two new roles with the new Revenue Engine – ‘Revenue Manager’ and ‘Revenue Accountant’
- The Revenue Manager defines key revenue recognition configurations and rules, and monitors and analyzes revenue results through various revenue reports.
- The Revenue Accountantprocesses daily revenue transactions, revenue recognition plans, and journal entries.
So how does this work?
Configure your revenue for these item types:
- Assembly including Serialized and Lot Numbered
- Download Item
- Kit/Package
- Inventory including Serialized and Lot Numbered
- Non-Inventory for Sale/Resale
- Other Charge for Sale/Resale
- Service for Sale/Resale
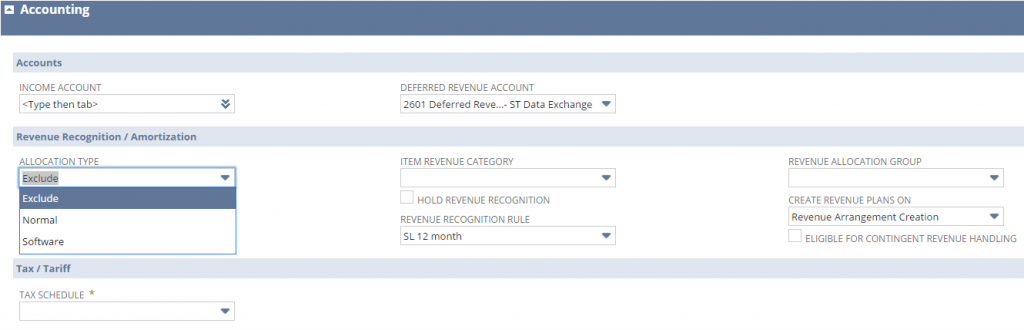
Item records must have values for:
- Revenue Recognition Rule
- Create Revenue Plans On
- Income Account
- Deferred Revenue Account – defaults in from the accounting preferences setup.
Other fields in the Revenue Recognition/Amortization group on the subtab are optional unless specifically required by an accounting preference or another feature.
These fields are in the Accounting subtab of the item – see below.
Once the invoice is created, the GL journal entry is created:
AR debit
Deferred Revenue credit
Next, you go to –
Management Revenue Arrangements and Management Revenue Plans
You set these to run automatically, or you can run this manually, whenever you need to generate revenue.
Transactions/Financial/
- Run Manage Revenue Arrangements
- Click ‘refresh.’ Once the status is ‘complete’ you go to –
- Manage Revenue Plans.
- Click ‘refresh.’ Status goes to ‘complete.’
Review the ‘plan’ for accuracy. This is an example of 6 months prorated based on the start date.
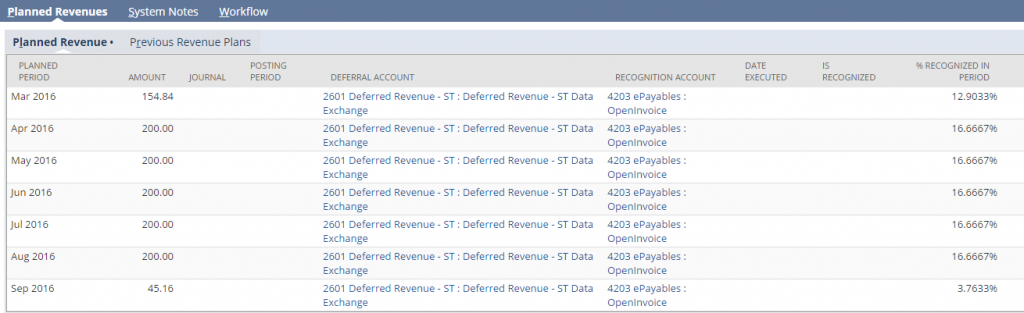
If you need to make changes to this rule, you can do so by running an ‘Update Revenue Recognition Plan.’ You can change the method and the start and end dates.
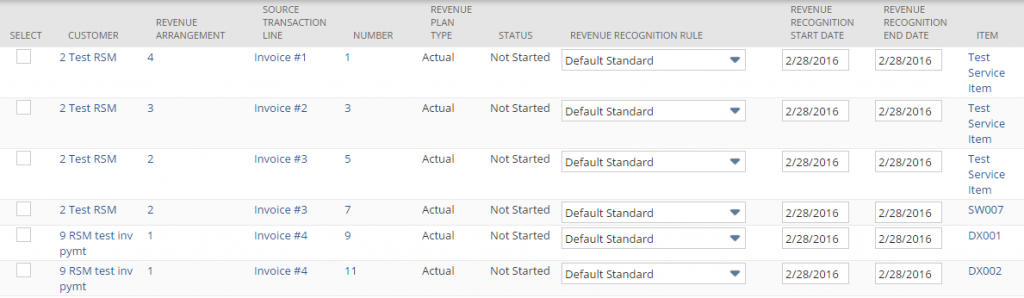
Select the line to edit by checking the ‘select’ box. Then edit the revenue recognition rule, start date, and end date. Click ‘submit.’
The revenue plan (schedule of months and amounts) will be updated based on the changes here.
Advanced Revenue Recognition For Project-Based Businesses –
This new Revenue engine can recognize revenue based on the percentage of completed project work by using percent-complete revenue recognition plans. A percent-complete plan is one that is derived from a percent-complete revenue recognition rule, using ‘Event-Percent Complete’ as their Amount Source.
Set up a service item to associate a percent-complete revenue recognition rule with your projects. Sales that contain the service item generate revenue recognition plans based on the rule and the linked project completion.
Also, time worked against the project and portions of the project are marked complete, journal entries are created to recognize the related revenue.
Revenue Reports –
The following reports are designed for revenue reconciliation purposes and tie to the general ledger account balances.
- Deferred Revenue by Customer Report
- Deferred Revenue by Item Report
- Revenue by Customer Report
- Revenue by Item Report
- Billing and Revenue Summary Report
- Deferred Revenue Rollforward Report
- Deferred Revenue Waterfall Summary Report
- Deferred Revenue Waterfall Detail Report
If you have any NetSuite customization or consulting needs, including this topic on revenue recognition as shown above, the NetSuite professionals at RSM can help. We are a NetSuite Solution Provider, and have more than 30 years experience implementing ERP solutions. We’ll provide you with industry insight, project management and the technical resources you need to make your project a success. Contact RSM at erp@rsmus.com or by phone at 855.437.7202 .
By: Brenda Moore – Colorado NetSuite Solutions Provider

 RSMUS.com
RSMUS.com